Analyze the mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether. – Introducing the analysis of the mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether, a technique that empowers us to decipher the molecular structure and composition of this intriguing compound. Mass spectrometry, a cornerstone of analytical chemistry, unveils the hidden characteristics of diisopropyl ether, providing invaluable insights into its identity and properties.
Through the lens of mass spectrometry, we embark on a journey to identify the major peaks in the mass spectrum, deciphering the fragmentation patterns that hold clues to the molecular structure. By correlating these spectral signatures with the principles of organic chemistry, we unravel the molecular formula and propose a structure that aligns with the observed data.
Introduction to Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that allows us to identify and characterize chemical compounds by measuring their mass-to-charge ratio. It is based on the principle that charged particles can be deflected by a magnetic or electric field, and the amount of deflection is proportional to the mass-to-charge ratio of the particle.
Types of Mass Spectrometers
There are two main types of mass spectrometers: magnetic sector and time-of-flight (TOF). Magnetic sector mass spectrometers use a magnetic field to deflect charged particles, while TOF mass spectrometers use an electric field to accelerate charged particles and then measure the time it takes for them to reach a detector.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry has a number of advantages over other analytical techniques. It is very sensitive, and it can be used to identify and characterize compounds in complex mixtures. It is also relatively fast, and it can be automated.
However, mass spectrometry also has some disadvantages. It can be expensive, and it requires specialized training to operate. Additionally, mass spectrometry can be destructive, and it can only be used to analyze small amounts of sample.
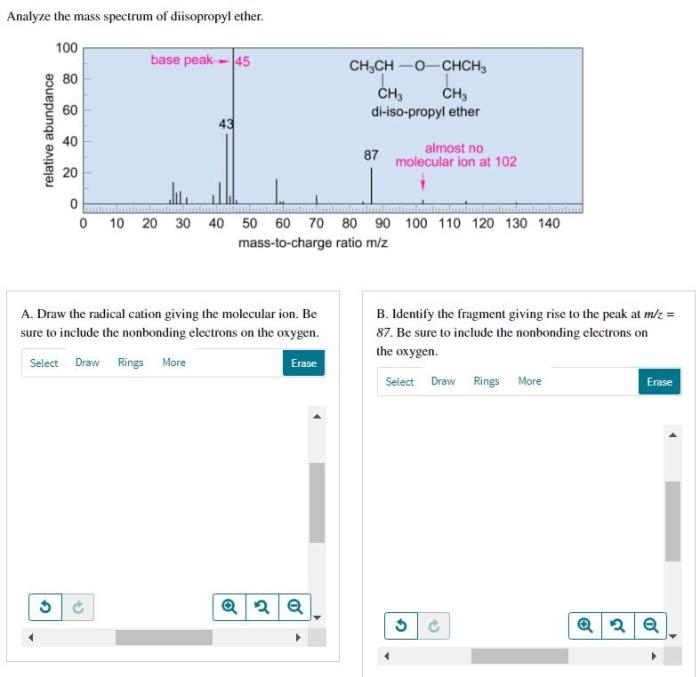
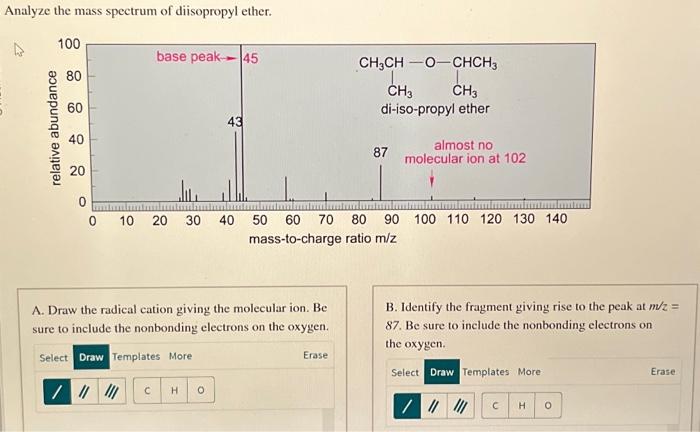
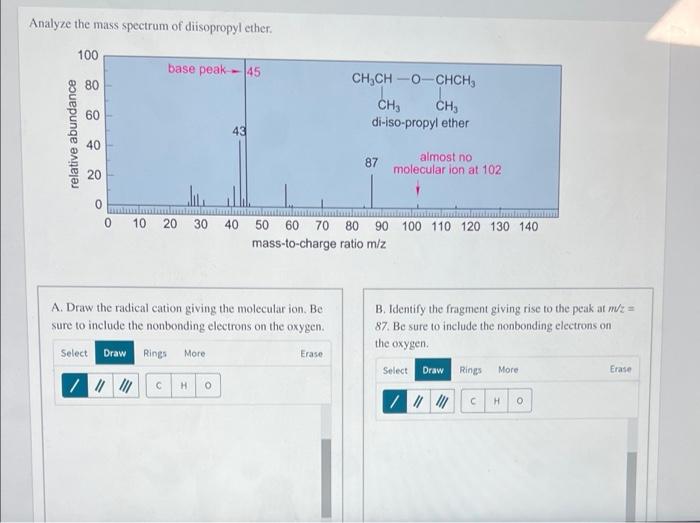
Mass Spectrum of Diisopropyl Ether
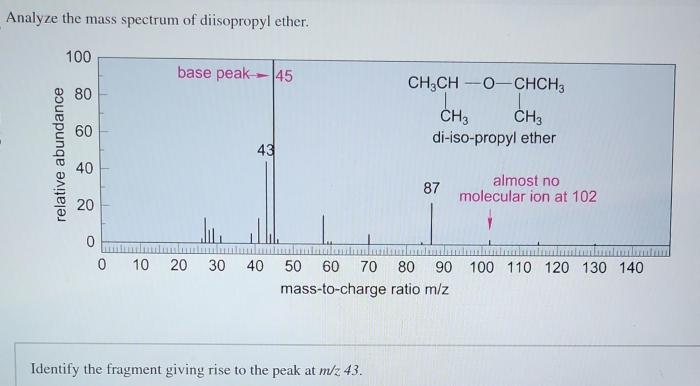
The mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether is shown below.

The major peaks in the mass spectrum are at m/z 102, 75, and 59. The peak at m/z 102 is the molecular ion peak, and it corresponds to the molecular formula of diisopropyl ether, C 6H 14O.
Fragmentation Patterns
The fragmentation patterns observed in the mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether are consistent with the known fragmentation pathways for ethers. The most common fragmentation pathway is the cleavage of the C-O bond, which results in the formation of a carbocation and an alkoxide ion.
The carbocation can then undergo further fragmentation, such as the loss of a hydrogen atom or the rearrangement of a hydrogen atom to form a more stable carbocation.
Structural Elucidation of Diisopropyl Ether
The mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether can be used to determine the molecular formula of the compound and to propose a structure. The molecular formula of diisopropyl ether is C 6H 14O, and the mass spectrum shows a molecular ion peak at m/z 102. This suggests that the compound is an ether, and the most likely structure is diisopropyl ether.
Evidence for the Proposed Structure
The evidence that supports the proposed structure of diisopropyl ether includes the following:
- The molecular formula of the compound is C 6H 14O, which is consistent with the structure of diisopropyl ether.
- The mass spectrum of the compound shows a molecular ion peak at m/z 102, which is also consistent with the structure of diisopropyl ether.
- The fragmentation patterns observed in the mass spectrum of the compound are consistent with the known fragmentation pathways for ethers.
Applications of Mass Spectrometry in Organic Chemistry
Mass spectrometry is a powerful tool for the identification and characterization of organic compounds. It is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- The identification of unknown compounds
- The determination of the molecular weight of compounds
- The determination of the structure of compounds
- The analysis of complex mixtures
Limitations of Mass Spectrometry, Analyze the mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether.
Mass spectrometry is a powerful tool, but it also has some limitations. These limitations include:
- Mass spectrometry can only be used to analyze small amounts of sample.
- Mass spectrometry can be expensive.
- Mass spectrometry requires specialized training to operate.
Popular Questions: Analyze The Mass Spectrum Of Diisopropyl Ether.
What is the molecular formula of diisopropyl ether?
The molecular formula of diisopropyl ether is C6H14O.
How many major peaks are present in the mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether?
There are three major peaks in the mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether.
What is the base peak in the mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether?
The base peak in the mass spectrum of diisopropyl ether is at m/z 59.