Which statement is true regarding neurons – Embarking on a quest to unravel the truth about neurons, this exploration delves into the intricate structure, electrical properties, and chemical signaling mechanisms that govern these remarkable cells. With meticulous precision and engaging prose, we unveil the secrets of neurons, unlocking their profound role in the symphony of our nervous system.
From the intricate structure of dendrites and axons to the dynamic interplay of ion channels, this discourse unravels the fascinating processes that enable neurons to transmit electrical signals and communicate with astonishing efficiency. Prepare to be captivated as we illuminate the fundamental principles that underpin neuronal function, shaping our understanding of the brain’s intricate workings.
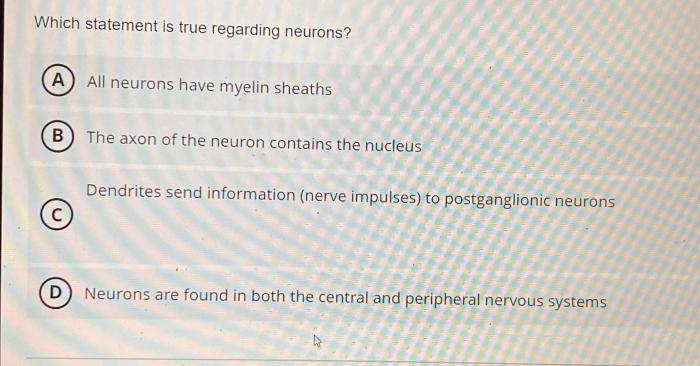
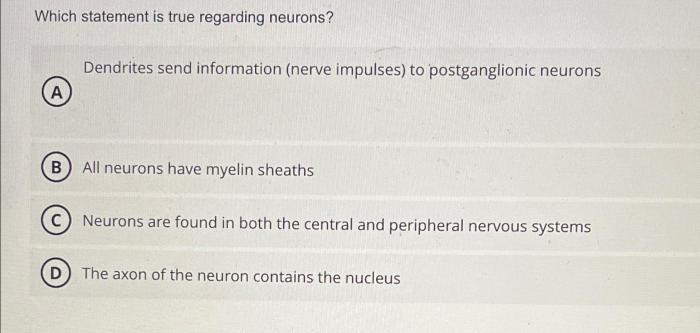
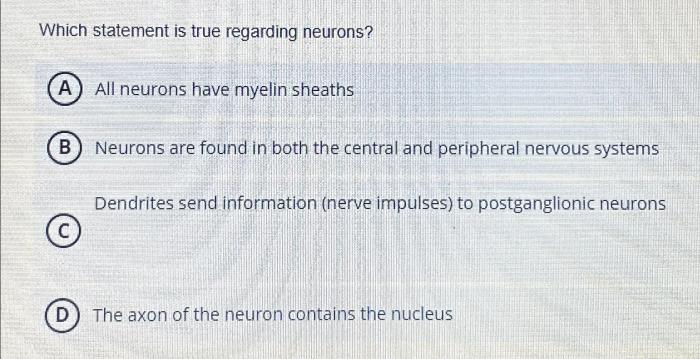
Definition and Structure of Neurons: Which Statement Is True Regarding Neurons
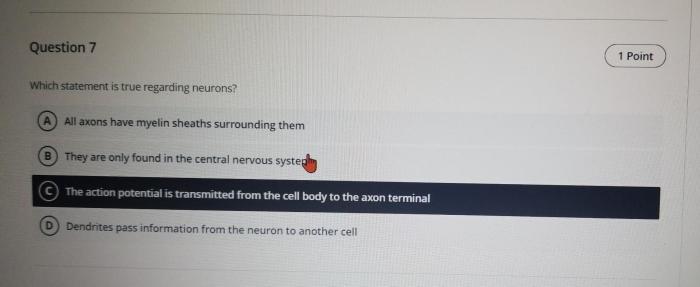
Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. They consist of three main components:
- Cell body (soma):Contains the nucleus, which houses the cell’s genetic material, and various organelles.
- Dendrites:Short, branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons.
- Axon:A long, slender projection that transmits signals away from the cell body to other neurons or target cells.
Each component plays a specific role in the transmission of electrical signals:
Electrical Properties of Neurons
Resting Membrane Potential:Neurons maintain a negative electrical potential across their cell membrane, known as the resting membrane potential. This potential is maintained by the differential distribution of ions across the membrane. Action Potential Generation:When a neuron receives a strong enough stimulus, the membrane potential rapidly depolarizes, leading to an action potential.
This is a brief, all-or-nothing electrical pulse that travels along the axon. Ion Channels:Ion channels are membrane proteins that regulate the flow of ions across the cell membrane. They play a crucial role in controlling the resting membrane potential and the generation and propagation of action potentials.
Chemical Signaling in Neurons, Which statement is true regarding neurons
Neurotransmitters:Neurons communicate with each other through the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These molecules are released from the axon terminals and bind to receptors on the dendrites of target neurons. Neurotransmitter Release:Action potentials trigger the release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles at the axon terminals.
Neurotransmitter Binding and Reuptake:Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the target neuron, influencing its electrical activity. After binding, neurotransmitters are either broken down or reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron.
Types and Classification of Neurons
Neurons can be classified based on various criteria, including:
| Criteria | Types | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Unipolar, Bipolar, Multipolar | Sensory neurons, Retinal neurons, Motor neurons |
| Function | Sensory, Motor, Interneurons | Touch receptors, Muscle cells, Neurons in the spinal cord |
| Location | Central (CNS), Peripheral (PNS) | Neurons in the brain and spinal cord, Neurons in the peripheral nerves |
Synaptic Plasticity and Learning
Synaptic Plasticity:Synaptic plasticity refers to the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, based on the frequency and pattern of activity. This is a fundamental mechanism underlying learning and memory. Long-Term Potentiation (LTP):LTP is a form of synaptic plasticity that results in a long-lasting increase in synaptic strength.
It is thought to play a role in learning and memory formation. Long-Term Depression (LTD):LTD is a form of synaptic plasticity that results in a long-lasting decrease in synaptic strength. It is thought to play a role in forgetting and synaptic pruning.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the primary function of neurons?
Neurons are specialized cells responsible for transmitting electrical and chemical signals throughout the nervous system, enabling communication between different parts of the body and brain.
How do neurons generate electrical signals?
Neurons generate electrical signals through a process called action potential, which involves a rapid change in the electrical charge across the neuron’s membrane, allowing for the transmission of signals over long distances.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in neuronal communication?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that are released by neurons to transmit signals across synapses, the junctions between neurons, enabling communication and information transfer within the nervous system.