Parliamentary procedure ffa cheat sheet, a concise and accessible resource for navigating the intricacies of parliamentary procedure, empowers individuals to conduct meetings with efficiency, transparency, and adherence to established rules. This comprehensive guide provides a clear understanding of the principles, practices, and special procedures that govern parliamentary meetings, ensuring effective decision-making and fostering productive discussions.
The following sections delve into the core elements of parliamentary procedure, including motions and amendments, voting and quorum, committees and subcommittees, meeting management, special rules and procedures, and the integration of electronic voting and meeting management systems. Each section is meticulously crafted to provide a thorough understanding of the topic, enabling readers to confidently navigate the complexities of parliamentary procedure and contribute meaningfully to meetings.
1. Parliamentary Procedure Overview
Parliamentary procedure is a set of rules and practices that govern the conduct of meetings and ensure the orderly and efficient transaction of business.
Its principles include respect for the rights of all participants, adherence to established rules, and the pursuit of the common good.
The chair presides over the meeting and ensures that the rules are followed, while participants have the right to participate in discussions and vote on motions.
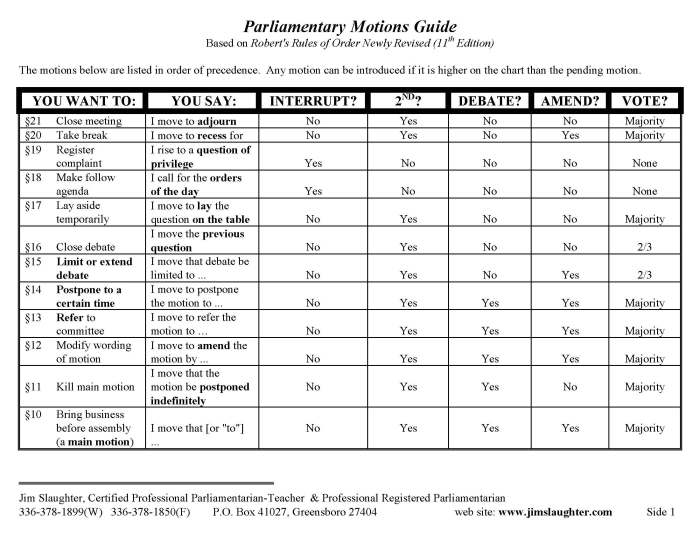
2. Motions and Amendments

Motions are formal proposals to take action on a specific matter.
Types of motions include:
| Motion | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Main Motion | To bring a new matter before the assembly |
| Subsidiary Motion | To modify or dispose of a main motion |
| Privileged Motion | To address urgent or important matters |
| Incidental Motion | To handle procedural matters |
Amendments are changes proposed to a motion before it is voted on.
The process of making and amending motions involves presenting the motion, discussing it, and voting on it.
3. Voting and Quorum
Voting methods include voice vote, show of hands, and roll call vote.
Quorum is the minimum number of members required to be present for a meeting to be valid.
If a quorum is not present, the meeting cannot proceed and any decisions made are void.
4. Committees and Subcommittees
Committees are smaller groups of members appointed to study specific issues and make recommendations.
Subcommittees are smaller groups formed by committees to focus on specific aspects of a larger issue.
Committees and subcommittees play a vital role in drafting resolutions and recommendations that are presented to the full assembly for consideration.
5. Meeting Management

Conducting a parliamentary meeting involves the following steps:
- Call to Order
- Approval of Agenda
- Reading of Minutes
- Reports of Officers
- Unfinished Business
- New Business
- Adjournment
Effective meeting management includes maintaining order, ensuring participation, and facilitating decision-making.
6. Special Rules and Procedures: Parliamentary Procedure Ffa Cheat Sheet
Special rules and procedures are used to address specific situations.
- Suspension of Rules: Allows for temporary suspension of the rules to address urgent matters.
- Reconsideration: Allows for a motion to be reconsidered after it has been voted on.
- Appeals: Allows for a ruling by the chair to be appealed to the assembly.
These rules are invoked when necessary to ensure the smooth and orderly conduct of meetings.
7. Electronic Voting and Meeting Management
Electronic voting and meeting management systems offer advantages such as:
- Increased accuracy and efficiency
- Enhanced transparency
- Remote participation
However, it is important to consider potential disadvantages such as technical issues and the need for training.
When used effectively, electronic systems can enhance the efficiency and transparency of parliamentary procedures.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of parliamentary procedure?
Parliamentary procedure provides a structured framework for conducting meetings, ensuring fairness, order, and the efficient conduct of business.
What is the role of the chair in a parliamentary meeting?
The chair presides over the meeting, maintains order, ensures adherence to rules, and facilitates discussion and decision-making.
How do I make a motion in a parliamentary meeting?
To make a motion, a participant must first obtain recognition from the chair, then state the motion clearly and concisely.
What is the difference between a motion and an amendment?
A motion is a proposal for action, while an amendment is a change or addition to a motion.
How do I vote in a parliamentary meeting?
Voting can be conducted by voice, show of hands, or secret ballot, depending on the rules of the meeting.